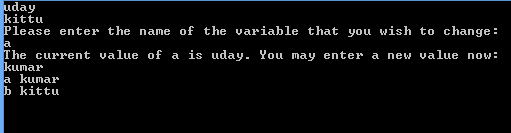
Reflection objects is used to obtaining type information at run time. With reflection we load field values. We loop through those fields and display their names and values.
System.Reflection,in the .NET Framework,provides a way to enumerate fields and properties. It can access fields by name.
The System.Reflection namespace contains classes that allow
you to obtain information about the application and to
dynamically add types, values and objects to the application.
Note:
Reflection is used get the metadata information of an assembly. Metadata (data about data) information means information about methods, properties, variables declared inside of an assembly not only it helps to retrieve information but also using reflection objects we can modify the type information and type behavior of an assembly at runtime.
namespace ConsoleApplication1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string test = "test";
Console.WriteLine(test.GetType().FullName);
Console.WriteLine(typeof(Int32).FullName);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
output:
Example
namespace ConsoleApplication1
{
static class A
{
public static int Height;
public static int Width;
public static int Weight;
public static string Name;
public static void Write()
{
Type type = typeof(A); // To get the type we use this
FieldInfo[] fields = type.GetFields(); //to get all fields
foreach (var field in fields)
{
string name = field.Name;
object temp = field.GetValue(null);
if (temp is int) //
{
int value = (int)temp;
Console.Write(name);
Console.Write(" (int) = ");
Console.WriteLine(value);
}
else if (temp is string)
{
string value = temp as string;
Console.Write(name);
Console.Write(" (string) = ");
Console.WriteLine(value);
}
}
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
A.Height = 1;
A.Width = 2;
A.Weight = 100;
A.Name = "Uday";
A.Write();
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
Output:

// Using GetType to obtain type information:
int i = 42;
System.Type type = i.GetType();
System.Console.WriteLine(type);
// Using Reflection to get information from an Assembly:
System.Reflection.Assembly info = typeof(System.Int32).Assembly;
System.Console.WriteLine(info);
namespace ConsoleApplication1{ public class MyObject { //public fields public string myStringField; public int myIntField; public MyObject myObjectField; } class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Type myObjectType = typeof(MyObject); System.Reflection.FieldInfo[] fieldInfo = myObjectType.GetFields(); foreach (System.Reflection.FieldInfo info in fieldInfo) Console.WriteLine(info.Name); Console.ReadKey(); } }}
Example 2:
public class MyObject { //public fields public string myStringField; public int myIntField; public MyObject myObjectField; } class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Type myObjectType = typeof(MyObject);
System.Reflection.FieldInfo[] fieldInfo = myObjectType.GetFields(); MyObject myObjectInstance = new MyObject();
//assigning the values. foreach (System.Reflection.FieldInfo info in fieldInfo) { switch (info.Name) { case "myStringField": info.SetValue(myObjectInstance, "string value"); break; case "myIntField": info.SetValue(myObjectInstance, 42); break; case "myObjectField": info.SetValue(myObjectInstance, myObjectInstance); break; } } //reading the values foreach (System.Reflection.FieldInfo info in fieldInfo) { Console.WriteLine(info.Name + ": " + info.GetValue(myObjectInstance).ToString()); } Console.ReadKey(); } }
Output:Example 3:
public class MyObject
{
//public properties
public string MyStringProperty { get; set; }
public int MyIntProperty { get; set; }
public MyObject MyObjectProperty { get; set; }
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Type myObjectType = typeof(MyObject);
//Get public properties
System.Reflection.PropertyInfo[] propertyInfo =
myObjectType.GetProperties();
foreach (System.Reflection.PropertyInfo info in propertyInfo)
Console.WriteLine(info.Name);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
Output:

Example 4
public class MyObject { //public events public event EventHandler MyEvent1; public event EventHandler MyEvent2; } class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Type myObjectType = typeof(MyObject); //Get events System.Reflection.EventInfo[] eventInfo = myObjectType.GetEvents();
foreach (System.Reflection.EventInfo info in eventInfo) Console.WriteLine(info.Name); Console.ReadKey(); }
}
Examplenamespace ConsoleApplication1{ class Program { static void FieldInvestigation(Type t) { Console.WriteLine("To get Fields in System"); FieldInfo[] fld = t.GetFields(); foreach (FieldInfo f in fld) { Console.WriteLine("{0}", f.Name); } }
static void MethodInvestigation(Type t) { Console.WriteLine("To get Methods in the System"); MethodInfo[] mth = t.GetMethods(); foreach (MethodInfo m in mth) { Console.WriteLine("-->{0}", m.Name); } } static void Main(string[] args) { Console.Write("Enter NameSpace"); string typName = Console.ReadLine(); Type t = Type.GetType(typName); FieldInvestigation(t); MethodInvestigation(t); Console.ReadKey(); } }}
Output:
Example:
File->New Project->Class Library
Write the following Code in Class1.cs as below
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace TestLibrary
{
public class Class1
{
public void Display()
{
Console.WriteLine("Welcome Uday");
}
}
}
Now, Build the Solution it Generates a dll File.
Now, Create a New Project to Consume that dll
File->New Project-Console Application
Write the following Code as follows:
namespace ConsoleApplication1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.Write("Please Enter Assembly Name:");
string typeName = Console.ReadLine();
try
{
Assembly assembly = Assembly.Load(typeName);
DisplayDetails(assembly);
}
catch
{
Console.WriteLine("Cannot Find Assembly");
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
static void DisplayDetails(Assembly assembly)
{
Console.WriteLine("Details in Assembly");
Console.WriteLine("Information:{0}", assembly.FullName);
Type[] type = assembly.GetTypes();
foreach (Type d in type)
{
Console.WriteLine("Type:{0}", d);
}
}
}
}
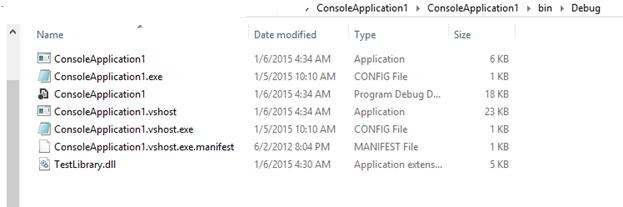
Now, copy the TestLibrary.dll into the Console Application \Bin\Debug Folder
as shown below
Now, Run the Program

Example:
namespace ConsoleApplication1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
try
{
Assembly asm = Assembly.LoadFrom(@"C:\TestLibrary.dll");
DispalyAssembly(asm);
}
catch
{
Console.WriteLine("Can't Load Assembly");
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
static void DispalyAssembly(Assembly assembly)
{
Console.WriteLine("Details in Assembly");
Console.WriteLine("Information:{0}", assembly.FullName);
Type[] type = assembly.GetTypes();
foreach (Type d in type)
{
Console.WriteLine("Type:{0}", d);
}
}
}
}
Output ...

Reflection Using Shared Assemblies.
Example:
namespace ConsoleApplication1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
try
{
string info = @"System.Windows.Forms," + "Version=4.0.0.0," +
"PublicKeyToken=B77A5C561934E089," +
@"Culture=""";
Assembly assembly = Assembly.Load(info);
Display(assembly);
}
catch
{
Console.WriteLine("Can't Load Assembly");
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
static void Display(Assembly assembly)
{
Console.WriteLine("Name:{0}", assembly.GetName().Name);
Console.WriteLine("Version:{0}", assembly.GetName().Version);
Console.WriteLine("Culture:{0}", assembly.GetName().CultureInfo.DisplayName);
Console.WriteLine("Loaded from GAC?:{0}", assembly.GlobalAssemblyCache);
}
}
}

Create instance from dynamically loaded assembly
Points to Remember:
To Load Assembly:
Assembly testAssembly = Assembly.LoadFrom(@"C:\TestLibrary.dll");
To get the type of Class from the Loaded Assembly.
Assembly testAssembly = Assembly.LoadFrom(@"C:\TestLibrary.dll");
Type calcType = testAssembly.GetType("TestLibrary.Class1");
To create instance of Class
Assembly testAssembly = Assembly.LoadFrom(@"C:\TestLibrary.dll");
Type calcType = testAssembly.GetType("TestLibrary.Class1");
object Instance = Activator.CreateInstance(calcType);
To get information about the property
Assembly testAssembly = Assembly.LoadFrom(@"C:\TestLibrary.dll");
Type calcType = testAssembly.GetType("TestLibrary.Class1");
object Instance = Activator.CreateInstance(calcType);
PropertyInfo numberPropertyInfo = calcType.GetProperty("Number");
Here Number is the get;set property in TestLibrary.dll
//To get value about the Property
Assembly testAssembly = Assembly.LoadFrom(@"C:\TestLibrary.dll");
Type calcType = testAssembly.GetType("TestLibrary.Class1");
object Instance = Activator.CreateInstance(calcType);
PropertyInfo numberPropertyInfo = calcType.GetProperty("Number");
double value = (double)numberPropertyInfo.GetValue(Instance, null);
Now I want to set the value of that property at Run time, Now the current value of
Number is 45.0, I am changing it to 10.0
Assembly testAssembly = Assembly.LoadFrom(@"C:\TestLibrary.dll");
Type calcType = testAssembly.GetType("TestLibrary.Class1");
object Instance = Activator.CreateInstance(calcType);
PropertyInfo numberPropertyInfo = calcType.GetProperty("Number");
numberPropertyInfo.SetValue(Instance, 10.0, null);
Example:
File->New Project->Class Library

Write the Following Code.
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace TestLibrary
{
public class Class1
{
private double _number=45.0;
public double Number { get { return _number; } set { _number = value; } }
}
}
Build the solution, it generated a .dll file.
Now, Create a New Project to Consume that dll
File->New Project-Console Application
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
try
{
Assembly testAssembly = Assembly.LoadFrom(@"C:\Users\UK2010013\Documents\visual studio 2012\Projects\TestLibrary\TestLibrary\bin\Debug\TestLibrary.dll");
Type calcType = testAssembly.GetType("TestLibrary.Class1");
object Instance = Activator.CreateInstance(calcType);
PropertyInfo numberPropertyInfo = calcType.GetProperty("Number");
double value = (double)numberPropertyInfo.GetValue(Instance, null);
Console.WriteLine("Number Value Before");
Console.WriteLine(value);
numberPropertyInfo.SetValue(Instance, 10.0, null);
Console.WriteLine("After Assigning Number Value");
double value2 = (double)numberPropertyInfo.GetValue(Instance, null);
Console.WriteLine(value2);
}
catch
{
Console.WriteLine("Can't Load Assembly");
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}