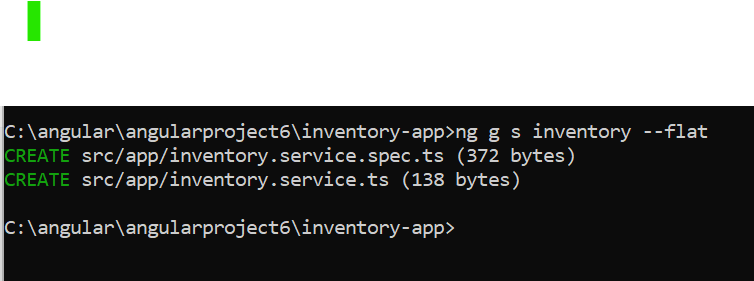
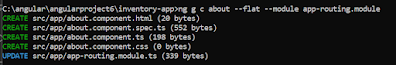
Requirement
Install Angular CLI and new Inventory -App
Let us create four new components, and we want to have it in the app-routing-module.ts
- AboutComponent
- AddproductComponent
- DisplayComponent
- DetailsComponent
Note:
In Realtime it is recommended to make AppModule[main module] as light weight by placing different components and routes into feature modules,this feature modules should be imported into AppModuleNow, if I create a About Component using ng g c About --flat--> Then it will import and place the component in the app ModuleNow, this examples requires1.create a product class 2.create a inventoryservice class[root|application level DI] 3.create components and routes into AppRoutingModule 4.import AppRoutingModule into AppModule [this will be done automatically] 5.design the mainpage and run the apptsconfig.json make the below changes in it... "strict": false ... "strictTemplates": false*create a class >ng g class productproduct.tsng g s inventory --flatBy default it comes under root level
Injectable decorator to a service class is mandatory for hierarchical and
application[or root] level DI, In real time it is recommended to apply
Injectable to a service class for any type of DI.create components into approutingmodule[goto app-routing.module.ts]:ng g c display --flat --module app-routing.moduleng g c about --flat --module app-routing.moduleng g c detail --flat --module app-routing.moduleng g c about --flat --module app-routing.moduleabout component.htmlAdd Products.htmlNote:Here we are using spread operator because>spread operator[...] create a new object based on pinfo object, this makes an object immutable.If i pass,
this._inventoryservice.addproduct(this.pinfo);In the next line we are clearing the values, so it will completely destroy the values in the array of pinfo(it will store in one address), so for that purpose we are using spread operator.Note: addproduct(pinfo) prods array pinfo-pid-p001 pname-xyz price-1000------------------------> address[pid-"" ..] this.pinfo.pid="" addproduct(new Product(pinfo.pid, pinfo.pname,pinfo.price))--->new object[pid-p001 ..] | {...this.pinfo}Display Component.ts1.FormsModule is required for ngModel directive[used in addproductcomponent] 2.CommonModule " " " *ngFor directive[used in displaycomponent]app.component.html