(7 methods explained)
Method 1:- Simple way
Method 2:- Override "OnException" method
Method 3:- Using "HandleError" Attribute
Method 4:- Inheriting from "HandleErrorAttribute"
Method 5:- Handling HTTP errors
Method 6:- Global Error handling in MVC
Method 7 : Should create a log file in the system
Method 1:- Simple way
But if we use this method then we will not be utilizing MVC exception mechanismproperly and completely.
public ActionResult SomeError() { try {} catch(Exception ex) {return View("Error");} }
Controller.
View
Output:

Method 2:- Override “OnException” method
This approach is used when we want to handle all the exceptions across the Action methods at the controller level.Controller
public ActionResult Test()
{
int x = 1, y = 0;
int z = x % y;
return View();
}
protected override void OnException(ExceptionContext filterContext)
{
Exception ex = filterContext.Exception;
filterContext.ExceptionHandled = true;
var model = new HandleErrorInfo(filterContext.Exception, "Controller", "Action");
filterContext.Result = new ViewResult()
{
ViewName = "Error",
ViewData = new ViewDataDictionary(model.Exception.Message)
};
}
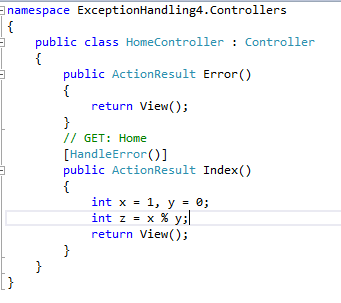
public ActionResult Error()
{
return View();
}
// GET: Home
public ActionResult Index()
{
int x = 1, y = 0;
int z = x % y;
return View();
}
Output:
Second Example:
protected override void OnException(ExceptionContext filterContext)
{
if (filterContext.ExceptionHandled || !filterContext.HttpContext.IsCustomErrorEnabled)
{
//return;
}
if (new HttpException(null, filterContext.Exception).GetHttpCode() != 500)
{
//return;
}
// if the request is AJAX return JSON else view.
if (filterContext.HttpContext.Request.Headers["X-Requested-With"] == "XMLHttpRequest")
{
filterContext.Result = new JsonResult
{
JsonRequestBehavior = JsonRequestBehavior.AllowGet,
Data = new
{
error = true,
message = filterContext.Exception.Message
}
};
}
else
{
var controllerName = (string)filterContext.RouteData.Values["controller"];
var actionName = (string)filterContext.RouteData.Values["action"];
var model = new HandleErrorInfo(filterContext.Exception, controllerName, actionName);
filterContext.Result = new ViewResult
{
ViewName = "Error",
ViewData = new ViewDataDictionary<HandleErrorInfo>(model),
TempData = filterContext.Controller.TempData
};
}
// log the error using log4net.
//_logger.Error(filterContext.Exception.Message, filterContext.Exception);
filterContext.ExceptionHandled = true;
filterContext.HttpContext.Response.Clear();
filterContext.HttpContext.Response.StatusCode = 500;
filterContext.HttpContext.Response.TrySkipIisCustomErrors = true;
}
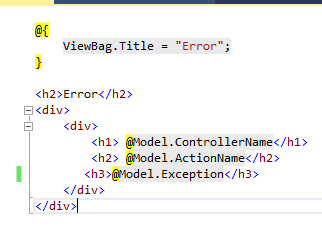
In the View write the following code
Output:
The problem with this approach is we cannot reuse the error handling logic across multiple controllers.
The other way of handling error is my using “HandleError” attribute. Implementing “HandleError” attribute is a two-step process:-
Step 1 :- We need to first decorate the action method with “HandleError” attribute as shown in the below code
public class HomeController : Controller
{
[HandleError()]
public ActionResult SomeError()
{
throw new Exception("test");
}
}
Step 2:- In the “Web.config” file you need to add the “customErrors” tag and point to the “Error” view as shown in the below “Web.config” code snippet.
Hide
<system.web>
<customErrors defaultRedirect="Error.cshtml" mode="On">
</customErrors>
</system.web>
public class HomeController : Controller
{
[HandleError(ExceptionType=typeof(ArithmeticException),View="Arthimetic")]
[HandleError(ExceptionType = typeof(NotImplementedException),View ="Error1")]
public ActionResult SomeError()
{
}
}
Still working on it..............................










No comments:
Post a Comment
Thank you for visiting my blog